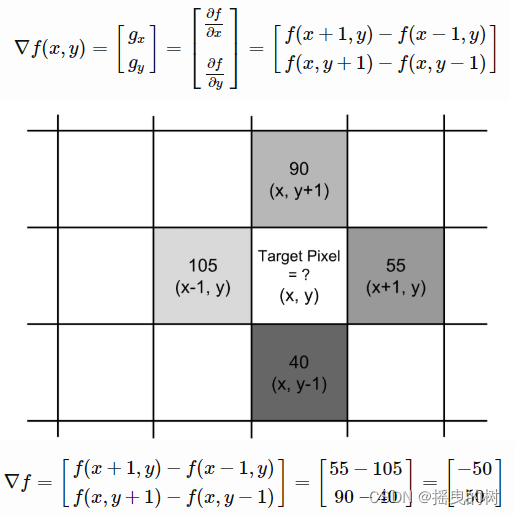
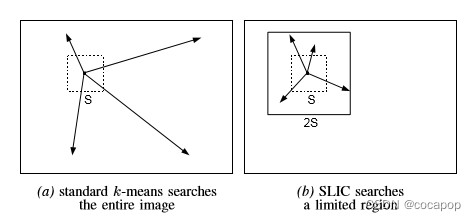
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
| import math
from skimage import io, color
import numpy as np
from tqdm import trange
class Cluster(object):
cluster_index = 1
def __init__(self, h, w, l=0, a=0, b=0):
self.update(h, w, l, a, b)
self.pixels = []
self.no = self.cluster_index
Cluster.cluster_index += 1
def update(self, h, w, l, a, b):
self.h = h
self.w = w
self.l = l
self.a = a
self.b = b
def __str__(self):
return "{},{}:{} {} {} ".format(self.h, self.w, self.l, self.a, self.b)
def __repr__(self):
return self.__str__()
class SLICProcessor(object):
@staticmethod
def open_image(path):
"""
Return:
3D array, row col [LAB]
"""
rgb = io.imread(path)
lab_arr = color.rgb2lab(rgb)
return lab_arr
@staticmethod
def save_lab_image(path, lab_arr):
"""
Convert the array to RBG, then save the image
:param path:
:param lab_arr:
:return:
"""
rgb_arr = color.lab2rgb(lab_arr)
io.imsave(path, rgb_arr)
def make_cluster(self, h, w):
h = int(h)
w = int(w)
return Cluster(h, w,
self.data[h][w][0],
self.data[h][w][1],
self.data[h][w][2])
def __init__(self, filename, K, M):
self.K = K
self.M = M
self.data = self.open_image(filename)
self.image_height = self.data.shape[0]
self.image_width = self.data.shape[1]
self.N = self.image_height * self.image_width
self.S = int(math.sqrt(self.N / self.K))
self.clusters = []
self.label = {}
self.dis = np.full((self.image_height, self.image_width), np.inf)
def init_clusters(self):
h = self.S / 2
w = self.S / 2
while h < self.image_height:
while w < self.image_width:
self.clusters.append(self.make_cluster(h, w))
w += self.S
w = self.S / 2
h += self.S
def get_gradient(self, h, w):
if w + 1 >= self.image_width:
w = self.image_width - 2
if h + 1 >= self.image_height:
h = self.image_height - 2
gradient = self.data[h + 1][w + 1][0] - self.data[h][w][0] + \
self.data[h + 1][w + 1][1] - self.data[h][w][1] + \
self.data[h + 1][w + 1][2] - self.data[h][w][2]
return gradient
def move_clusters(self):
for cluster in self.clusters:
cluster_gradient = self.get_gradient(cluster.h, cluster.w)
for dh in range(-1, 2):
for dw in range(-1, 2):
_h = cluster.h + dh
_w = cluster.w + dw
new_gradient = self.get_gradient(_h, _w)
if new_gradient < cluster_gradient:
cluster.update(_h, _w, self.data[_h][_w][0], self.data[_h][_w][1], self.data[_h][_w][2])
cluster_gradient = new_gradient
def assignment(self):
for cluster in self.clusters:
for h in range(cluster.h - 2 * self.S, cluster.h + 2 * self.S):
if h < 0 or h >= self.image_height: continue
for w in range(cluster.w - 2 * self.S, cluster.w + 2 * self.S):
if w < 0 or w >= self.image_width: continue
L, A, B = self.data[h][w]
Dc = math.sqrt(
math.pow(L - cluster.l, 2) +
math.pow(A - cluster.a, 2) +
math.pow(B - cluster.b, 2))
Ds = math.sqrt(
math.pow(h - cluster.h, 2) +
math.pow(w - cluster.w, 2))
D = math.sqrt(math.pow(Dc / self.M, 2) + math.pow(Ds / self.S, 2))
if D < self.dis[h][w]:
if (h, w) not in self.label:
self.label[(h, w)] = cluster
cluster.pixels.append((h, w))
else:
self.label[(h, w)].pixels.remove((h, w))
self.label[(h, w)] = cluster
cluster.pixels.append((h, w))
self.dis[h][w] = D
def update_cluster(self):
for cluster in self.clusters:
sum_h = sum_w = number = 0
for p in cluster.pixels:
sum_h += p[0]
sum_w += p[1]
number += 1
_h = int(sum_h / number)
_w = int(sum_w / number)
cluster.update(_h, _w, self.data[_h][_w][0], self.data[_h][_w][1], self.data[_h][_w][2])
def save_current_image(self, name):
image_arr = np.copy(self.data)
for cluster in self.clusters:
for p in cluster.pixels:
image_arr[p[0]][p[1]][0] = cluster.l
image_arr[p[0]][p[1]][1] = cluster.a
image_arr[p[0]][p[1]][2] = cluster.b
image_arr[cluster.h][cluster.w][0] = 0
image_arr[cluster.h][cluster.w][1] = 0
image_arr[cluster.h][cluster.w][2] = 0
self.save_lab_image(name, image_arr)
def iterate_10times(self):
self.init_clusters()
self.move_clusters()
for i in trange(10):
self.assignment()
self.update_cluster()
name = 'lenna_M{m}_K{k}_loop{loop}.png'.format(loop=i, m=self.M, k=self.K)
self.save_current_image(name)
if __name__ == '__main__':
p = SLICProcessor('Lenna.png', 200, 40)
p.iterate_10times()
p = SLICProcessor('Lenna.png', 300, 40)
p.iterate_10times()
p = SLICProcessor('Lenna.png', 500, 40)
p.iterate_10times()
p = SLICProcessor('Lenna.png', 1000, 40)
p.iterate_10times()
p = SLICProcessor('Lenna.png', 200, 5)
p.iterate_10times()
p = SLICProcessor('Lenna.png', 300, 5)
p.iterate_10times()
p = SLICProcessor('Lenna.png', 500, 5)
p.iterate_10times()
p = SLICProcessor('Lenna.png', 1000, 5)
p.iterate_10times()
|